Gynaecology involves dealing with the health of the female reproductive system (uterus, vagina, and ovaries). Experienced surgeons at Ashirvad hospital work with state-of-the-art equipment and perform both simple and complex procedures in gynaecology in laparoscopic way.
Pregnancy which occurs outside the uterus (womb), usually in one of the fallopian tubes, is termed Ectopic. It is also known as Tubal pregnancy. It may even grow in ovaries or abdomen. There is no way to save an ectopic pregnancy. It cannot turn into a normal pregnancy. If the egg keeps growing in the fallopian tube, it can damage or burst the tube and cause heavy bleeding that could be deadly. It happens in about 0.02% pregnancies in India. This is a medical emergency and can be fatal.
Pelvic or belly pain. It may be sharp on one side at first and then spread through belly. It may be worse when trying to move or strain. Vaginal bleeding.
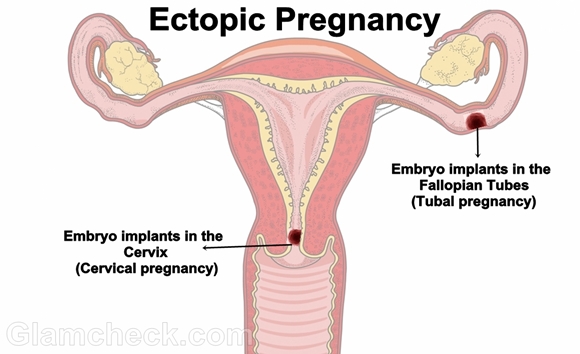
An ectopic pregnancy is often caused by damage to the fallopian tubes. A fertilized egg may have trouble passing through a damaged tube, causing the egg to implant and grow in the tube. Things that make you more likely to have fallopian tube damage and an ectopic pregnancy include:
Smoking. The more you smoke, the higher your risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is often the result of an infection such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Endometriosis, which can cause scar tissue in or around the fallopian tubes.
Both the partners need to be evaluated for infertility problems and the individual problems need to be addressed.
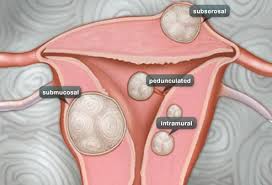
Fibroids are non-cancerous tumours of the uterus found in almost 25% of women in the reproductive age group (25-50 years of age).
Excessive bleeding during periods
Feelings of heaviness in abdomen and lethargy
Abdominal pain
Lump in the abdomen in the cases of large fibroids
Difficulty in passing urine
Constipation
The reasons why women get fibroids aren’t known. Although oestrogen seems to make fibroids grow, it’s not thought to be responsible for their initial development. You’re more likely to get fibroids if you:
have a mother or sister who has fibroids
have no children – pregnancy and childbirth seem to protect against developing fibroids experience early onset of periods are overweight – some studies have suggested a link between being overweight and developing fibroids.
Watch the Symptoms– If the fibroids are small and not giving rise to any symptoms, no active treatment is required. The patient is advised for regular annual ultrasound check up to monitor the size of the fibroid(s).
Medications– These can be given to shrink the fibroids temporarily so as to control symptoms such as painful or heavy periods. But, this is not a permanent cure for fibroids.
Surgery– This option is offered when the symptoms are not being controlled with medications or in case the fibroids are too big/growing too rapidly.
Laparoscopic Myomectomy– This is indicated when the female is young and wants to preserve her uterus. Through this keyhole surgery the myoma or the fibroid is removed. This procedure leaves no long scar, so better cosmetic results are obtained.
Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy– If the women has completed her family & is having multiple fibroids, then the uterus is removed along with the fibroids.
Hysteroscopic Myomectomy– If the fibroid is encroaching the uterine cavity (i.e submucus in position), then this procedure is opted where a small telescope with instruments is introduced from below into uterus and the fibroid is shaved off , this can be done for small fibroids and there is no incision on the abdomen.
Post surgery patient should not lift heavy weights for 4-6 weeks. Preferably the person is advised to avoid cough and constipation. Patient is advised to delay pregnancy after myomectomy for 9-12 months.
Ovarian cysts are fluid filled sacs inside the ovary. ‘Large’ or ‘pathological cysts’ can occur in about 5% of women during their reproductive years. Ovarian cysts are common, frequently asymptomatic and often resolve spontaneously.
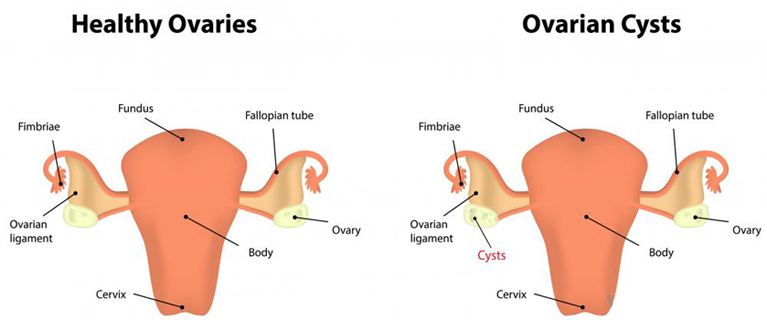
Often asymptomatic.
Mild menstrual irregularities & vague pelvic pain.
Low abdominal swelling.
Pain in case torsion, rupture or haemorrhage occurs.
Amenorrhoea (no menses), obesity & hirsutism (hair growth on abnormal body parts) may be the presenting picture.
Occasional dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse) may also be present.
Follicular cyst: This results from the growth of a follicle. A follicle is the normal fluid-filled sac that contains an egg. Follicular cysts form when the follicle grows larger than normal during the menstrual cycle and does not open to release the egg. Usually, follicular cysts resolve spontaneously over the course of days to months.
Luteum cyst: The corpus luteum is an area of tissue within the ovary that occurs after an egg has been released from a follicle. If a pregnancy doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum usually breaks down and disappears. It may, however, fill with fluid or blood and persist as a cyst on the ovary. Usually, this cyst is found on only one side, produces no symptomsand resolves spontaneously.
Endometriosis is a condition in which cells that normally grow inside as a lining of the uterus (womb), instead grow outside of the uterus in other locations. When endometriosis involves the ovary, the area of endometrial tissue may grow and bleed over time, forming a blood-filled cyst. The condition known as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts within both ovaries. PCOS is associated with a number of hormonal problems and is the most common cause of infertility in women.
Infections of the pelvic organs can involve the ovaries and Fallopian tubes. In severe cases, pus-filled cystic spaces may be present on or around the ovary or tubes. These are known as tubo-ovarian abscesses.
Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy – Laparoscopic ovarian cyst excision is the procedure done to treat simple ovarian cysts. It is a safe procedure & does not need more than 1 day stay in the hospital, which is an advantage for young girls.
Laparoscopy Ovarian Drilling – This is done in case of polycystic ovaries wherein the multiple cysts on the surface of the ovary are drilled.
Oophorectomy – Removal of the ovary along with the pathological cyst. This is done when the cyst is big & involves the whole ovary.
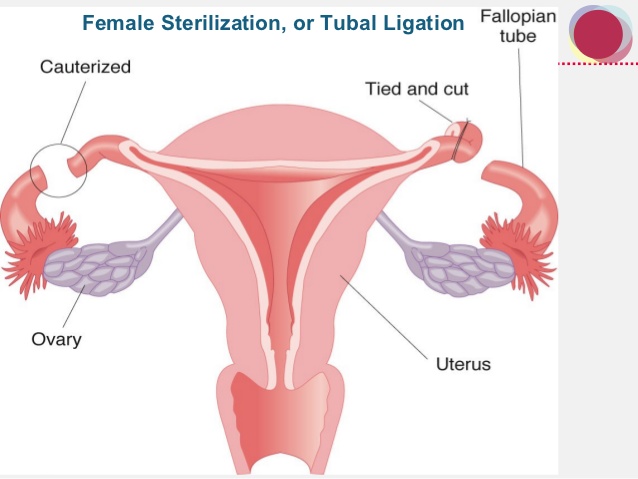
Tubal sterilization results in mechanically blocking or interrupting the fallopian tubes to prevent sperm from fertilizing the egg.
Pelvic infection
Tubal endometriosis
Previous abdominal surgeries
Intra uterine contraceptives
One-sided, intense, persistent pain in lower abdomen.
Collapse, preceded by dizziness, diarrhoea, vomiting, and/or pain.
Vaginal bleeding.
Shoulder-tip pain: This may occur in case of internal bleeding which irritates other internal body organs such as diaphragm.
Pain in lower back.
Pain while passing urine or stool.
include laparoscopy & laparotomy. Laparotomy is an open procedure whereby a transverse incision is made across the lower abdomen. Laparoscopy is preferred over laparotomy because of tiny incisions and speedy recovery. We prefer treating such patients with laparoscopy as recovery is faster.
Tubal sterilization is indicated for women who want a permanent method of contraception and are free of any gynecologic pathology that would otherwise dictate an alternate procedure. Tubal sterilization is also indicated for women in whom a pregnancy could represent a significant clinical and medical risk.
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus (womb) and is performed when a woman has uterus related problems after her child bearing is complete.
Severe pain
Heavy bleeding during periods
Other damaged organs
The presence of fibroids
The prolapse of the uterus (where the uterus is shifted from its usual position)
Endometriosis (presence of the uterine lining in nearby organs causing severe pain and bleeding)
Uterine or cervical cancer
Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy– If the women has completed her family & nearing her menopause , then the uterus is removed laparoscopically. Vaginal hysterectomy– This is usually done in case of prolapsed and small size uterus and the uterus is removed from below through the birth passage. Follow up
Post surgery patient should not lift heavy weights for 4-6 weeks. Preferably the person is advised to avoid cough and constipation. Patient may develop postmenopausal symptoms like hot flashes , mood swings which subside by itself. If severe then they may need medications.
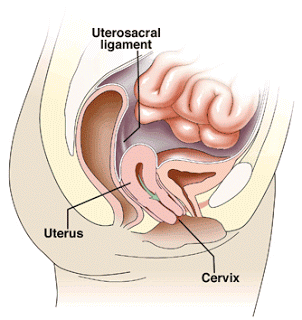
Uterine Prolapse is the downward displacement of any pelvic organ from its normal position. It usually involves the uterus and along with it bladder or rectum may also be involved. Complete Pelvic organ Prolapse is known as Procidentia. Uterine Prolapse is most often attributed to childbirth injury or it may be due to inherent weakness of suspensary ligaments. Prolapse manifests most commonly after menopause when the production of ovarian hormones gradually stops and genital support weakens.
Feeling of a lump coming out of the vaginal orifice.
Dragging sensation in the pelvis, especially at end of day.
Backache.
Difficulty in walking.
Difficulty in intercourse.
Concomitant stress incontinence or frequency, inadequate emptying of bladder, repeated urinary tract infection.
Difficulty in defecation & constipation.
Pelvic organ prolapse is usually caused by damage to the tissues (muscles, ligaments, and connective tissue) that support the pelvic organs. Damage or stretching of these tissues allows the organs to move out of their normal positions. This causes them to press against (and sometimes move) the inside walls of the vagina.
Having a baby makes it more likely that you will have pelvic organ prolapse later. Vaginal childbirth has been strongly linked to weakened and stretched support structures in the pelvic area. This loss of support is the biggest cause of pelvic organ prolapse. Having a cesarean section, seems to be less strongly linked to pelvic organ prolapse. Another cause of reduced support in the pelvis is lower levels of the hormone estrogen. Estrogen levels are lower during and after menopause. The lower levels of estrogen in the body mean less collagen, a protein that helps the pelvic connective tissues stretch and return to their normal positions.
Expectant Management – Uterine Prolapse may be discovered during a routine gynaecological examination. Such patients may not have any symptoms. They are advised for buttock squeezing exercises or Kegel exercises. In post-menopausal women, use of estrogen cream may also help to strengthen the support.